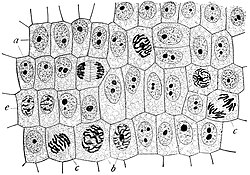
 Most distinct cell types arise from a single totipotent cell, called a zygote, that differentiates into hundreds of different cell types during the course of development.
Most distinct cell types arise from a single totipotent cell, called a zygote, that differentiates into hundreds of different cell types during the course of development. A cell is a mass of cytoplasm that is bound externally by a cell membrane. Usually microscopic in size, cells are the smallest structural units of living matter and compose all living things. Most cells have one or more nuclei and other organelles that carry out a variety of tasks.
A cell is a mass of cytoplasm that is bound externally by a cell membrane. Usually microscopic in size, cells are the smallest structural units of living matter and compose all living things. Most cells have one or more nuclei and other organelles that carry out a variety of tasks. Human cells contain the following major parts, listed in alphabetical order: Within cells, the cytoplasm is made up of a jelly-like fluid (called the cytosol) and other structures that surround the nucleus. The cytoskeleton is a network of long fibers that make up the cell’s structural framework.
Human cells contain the following major parts, listed in alphabetical order: Within cells, the cytoplasm is made up of a jelly-like fluid (called the cytosol) and other structures that surround the nucleus. The cytoskeleton is a network of long fibers that make up the cell’s structural framework.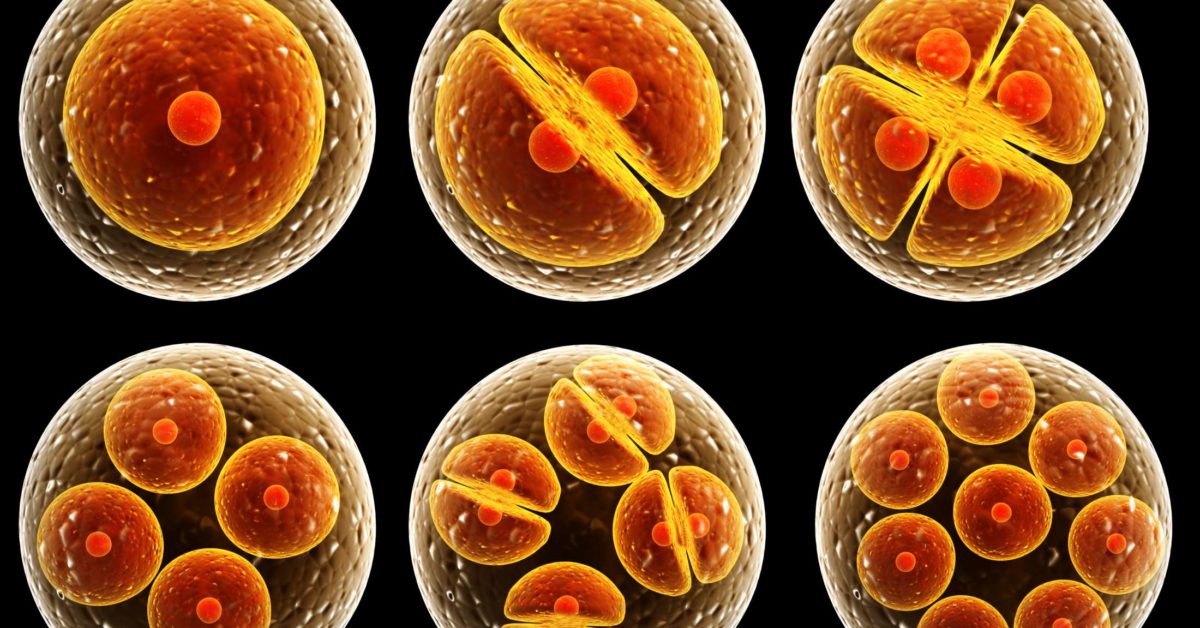 Cells are the basic units of life. The body contains trillions of cells, which vary widely in size, number, structure, and function. Cells also communicate with each other. Whether in plants,...
Cells are the basic units of life. The body contains trillions of cells, which vary widely in size, number, structure, and function. Cells also communicate with each other. Whether in plants,... We publish research across all areas of science, inspiring new directions from fundamental discoveries to technological breakthroughs. We’re committed to supporting authors and streamlining the publication process to help you find the right home for your research.
We publish research across all areas of science, inspiring new directions from fundamental discoveries to technological breakthroughs. We’re committed to supporting authors and streamlining the publication process to help you find the right home for your research.